FUELLING THE BODY FOR EXCELLENCE
If you want to perform well then you need to fuel yourself properly for every workout. Whether that is a heavy strength session, a longer endurance race or a high intensity CrossFit® WOD, you need to go into the workout with well established energy levels that will help you perform at the top of your game.
UNDERSTANDING ENERGY
After we eat, our bodies digest the food by mixing it with fluids (acids and enzymes) in the stomach. When the stomach digests food, the carbohydrate (sugars and starches) in the food breaks down into another type of sugar, called glucose.
The stomach and small intestines absorb the glucose and then release it into the bloodstream. Once in the bloodstream, glucose can be used immediately for energy or stored in our bodies, to be used later.
The body has several different ways of providing energy during exercise. Dependent on the intensity and/or duration of activity – the body can provide energy through aerobic or anaerobic metabolism.
The three energy systems under this umbrella are the ATP-PC System (immediate energy), the Glycolytic system (short term energy), and the Oxidative system (long term energy).
Each has a specific means of providing energy dependent on the body’s requirements.
TYPES OF SUGAR
- Glucose – It occurs naturally in plants and fruits and is a by-product of photosynthesis. Our bodies burn glucose as energy, or it can convert it into glycogen (essentially: liver and muscle fuel). And our bodies can actually produce glucose when needed.
- Fructose – Fruit sugar. It also occurs naturally in cane sugar and honey and is incredibly sweet. While this is a natural sugar, our body cannot produce it, and it can be difficult to break down in large quantities. It is broken down by our liver, but when it is over consumed our liver can become overloaded and so it is instead turned into fat and stored in our body.
- Sucrose – Found in the stems of sugarcane, and is essentially half glucose and half fructose.
- Lactose – Milk sugar.
HOW EXCESSIVE SUGAR CAN NEGATIVELY AFFECT THE BODY
Sugar causes glucose levels to spike and plummet.
Unstable blood sugar levels can cause mood swings, fatigue, cravings and headaches.
Sugar increases the risk of obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
Foods that quickly affect blood sugar levels will heighten the risk of obesity, heart disease, and diabetes.¹
Emerging research also suggests connections between these high-glycemic diets and various forms of cancer.²³
Sugar accelerates aging
Sugar can also affect the quality of your skin by contributing to wrinkles and sagging. After sugar is absorbed into your bloodstream, it attaches to proteins. The mix of these proteins with sugar causes the skin to lose elasticity and can lead to premature aging.§
COUNTERING THESE NEGATIVE CONSEQUENCES
SweetLeaf® Stevia is a healthy alternative to added sugars, a great alternative to help you reduce your sugar intake in a natural way. With no artificial sweeteners, no sugars, no carbohydrates, and a non-glycemic response, SweetLeaf adds tasty sweetness to everything from hot and cold beverages to foods and recipes.
Obviously reducing the intake of added sugars will lessen the possibility of the effects described above. It is better to approach this gradually and change eating habits over time. Making a drastic change is a technique that is often prone to failure in the long run. Consistency is the key. SweetLeaf is a great way to lower your intake in a way that is sustainable. You don’t need to radically alter habits, rather adapt and replace added sugars with this healthy alternative.
5 HEALTHY PRE-WORKOUT ENERGY SOURCES
The following foods are all great sources of nutrition for energy (and more) before training. They include both fast acting and slow burning energy sources to suit the requirements of your respective sporting discipline and goals.
1. DATES
Dates are a great source of fibre, carbohydrate, potassium, magnesium and energy. They are also exceptionally popular in the endurance marathon and triathlon scenes, and for good reason.
Eat a handful 5 – 10 minutes before you start training. Use them as a snack during longer races or swims when you need a fast-acting boost of energy.
2. OATS
Oats offer effective slow releasing energy, complex carbohydrates, protein and a good source of the soluble fibre beta-glucan.
Combine them with natural yoghurt and a handful of fruit. At times they can taste bland and uninspiring so add SweetLeaf® Stevia drops (link) in chocolate or vanilla crème to make the meal much more delicious.
Consume a meal like this 1 – 1.5 hours before a workout.
3. FRUIT SMOOTHIES
A tasty source of fast-acting glucose. Add in protein powder to help prevent muscle catabolism whilst you train. The following fruits all work well.
Blueberries – As well as providing a quick shot of energy, blueberries can help heart health, bone strength, skin health and blood pressure.
Apricots – These contain calcium, potassium, phosphorus, vitamin A, iron and vitamin C. One cup serving of dried apricots contains 158 micrograms of vitamin A and will help raise your energy levels for your training.
Bananas – The powerful combination of complex carbohydrates, natural sugar, amino acids and minerals make it a beneficial food for athletes. Bananas are a fast-acting energy source perfect for fuelling athletic performance.
Smoothie Recipe
- 4 ice cubes
- ¼ fresh pineapple – peeled, cored and cubed
- 1 large banana – cut into chunks
- 1 cup of apple juice
- 1 squeeze of raspberry lemonade Stevia water enhancer
Add all ingredients into a mixer and blend. Pour and serve with a sprig of mint.
Macronutrients per serving:
- 313 calories
- 9 g fat
- 7 g carbohydrates
- 3 g protein
- 0 mg cholesterol
- 10 mg sodium
4. ORGANIC SWEET POTATOS
Sweet potatoes are a great source of complex carbohydrates that should be consumed around 2-3 hours pre-workout. Try baking sweet potato chips for a delicious and healthy snack.
5. COFFEE
Coffee is one of the most commonly used stimulants in the world. Caffeine blocks an inhibitory neurotransmitter in your brain, causing a stimulant effect. This improves energy levels, mood and various aspects of brain function.
Whether you prefer it black or with soya, lactose free or regular milk, replace any sugar you might be tempted to add with SweetLeaf® Stevia Tabs®. They will sweeten your coffee without adding any calories or carbs.
HYDRATION, HEALTH AND PERFORMANCE
When working out it is absolutely essential to stay hydrated.
‘A 2% loss of fluid can result in a decrease of athletic performance up to 10-20%.’
Water is used for cooling the body, so a lack of hydration can lead to fatigue, which of course, affects performance. Dehydration levels of as little as 3% can lead to physiologic dysfunction and increase the chances of an athlete developing a heat illness from exhertion (i.e. heat cramps, heat exhaustion, even heat stroke).
If you find water bland, and often forget to drink enough, then flavoured sweeteners are a great way to encourage you to enjoy staying hydrated pre, intra and post workout.
Reducing personal intake of added sugars is an important step on the road to a healthier you.
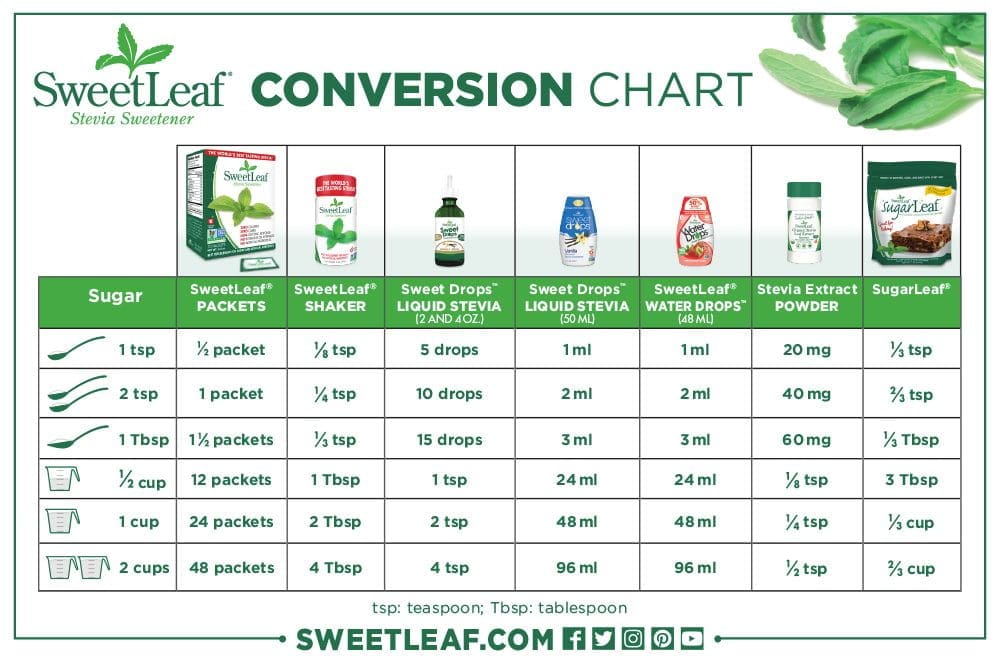
Use the measurements below to see how easily you can also replace sugar in baking and other recipes.
¹ Bell, S.J., Sears, B., “Low-glycemic-load diets: impact on obesity and chronic diseases.” Critical Reviews in Food Science & Nutrition, 43(4), 2003, pages 357-77.
² Michaud, D.S., Liu, S., Giovannucci, E., et al., “Dietary Sugar, Glycemic Load, and Pancreatic Cancer Risk in a Prospective Study.” Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 94(17), 2002, pages 1293-1300.
³ Romieu, I., Lazcano-Ponce, E., Sanchez-Zamorano, L.M., et al., “Carbohydrates and the Risk of Breast Cancer Among Mexican Women.” Cancer Epidemiology and Biomarkers Preview, 13(8), 2004, pages 1283-1289.
§ Sensi, M., Pricci, F., Andreani, D., et al., “Advanced Nonenzymatic Glycation Endproducts (AGE): Their Relevance to Aging and the Pathogenesis of Late Diabetic Complications.” Diabetes Research, 16(1), 1991, pages 1-9.